I recently purchased a Synology DS920+ NAS to use as a host for Linux containers and manage it via the Docker API and Terraform. This post is how I got the device to do exactly that. As to the name of the device, it is named after a ReBoot character.

Overview
The Synology DSM Docker interface makes use of the UNIX socket to communicate with Docker daemon (dockerd). So, we will include this in the list of host endpoints when making the modifications, if not we will lose use of the DSM Docker interface.
Enable SSH Access
To enable SSH Access to the NAS, you can find this under Terminal & SNMP > Enable SSH service. Check the box and click Apply to have the SSH service started.
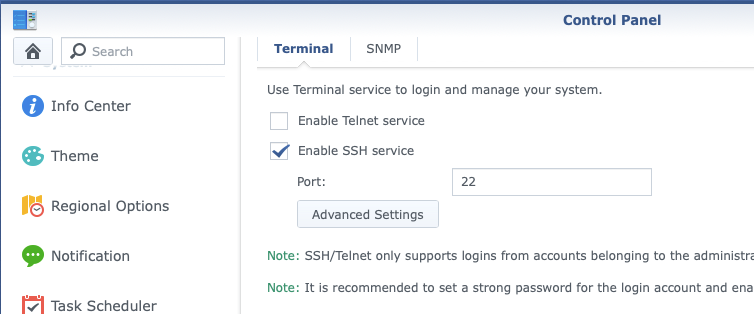
Once enabled, use a SSH client to connect using the password choosen when setting up the NAS device. You remember that don’t you?
~/ ssh admin@phong
admin@phong's password:
Could not chdir to home directory /var/services/homes/admin: No such file or directory
admin@phong:/$ uname -a
Linux phong 4.4.59+ #25426 SMP PREEMPT Mon Dec 14 18:48:52 CST 2020 x86_64 GNU/Linux synology_geminilake_920+
admin@phong:/$
Docker Daemon Configuration Changes
Once logged in to the NAS device, proceed to the packages directory (/var/packages) and edit the Docker package Docker/etc/dockerd.json file to get
UNIX sockets and a TCP endpoint. You will want to include the UNIX socket entry, as this is what the Docker DSM interface uses, not including it will prevent the showing of statistics, containers, and images. The TCP
socket is used by remote Docker clients.
The package Docker configuration file can be found at /var/packages/Docker/etc/dockerd.json
{
"data-root" : "/var/packages/Docker/target/docker",
"log-driver" : "db",
"registry-mirrors" : [],
"storage-driver" : "btrfs",
"hosts" : [ "unix:///var/run/docker.sock", "tcp://0.0.0.0:2375" ]
}
This configuration is insecure, it allows any client over a plaintext connection, a clear no-no today. Continue on how to secure the endpoint.
Endpoint Security
Beware that the default setup provides un-encrypted and un-authenticated direct access to the Docker API, which is just like having root - and should be secured either using the built in HTTPS encrypted socket, or by putting a secure web proxy in front of it.
The parameters of dockerd to use TLS, you will need the CA, docker certificate (I use the default Synology certificate), and certificate private key.
Note: I have internal CA that I used to issue certificate to my NAS device. This is a simple CA service running on OPNsense device.
...
--tls Use TLS; implied by --tlsverify
--tlscacert string Trust certs signed only by this CA (default "/root/.docker/ca.pem")
--tlscert string Path to TLS certificate file (default "/root/.docker/cert.pem")
--tlskey string Path to TLS key file (default "/root/.docker/key.pem")
--tlsverify Use TLS and verify the remote
...
Synology DSM stores certificates at this path
root@phong:/# ls /usr/syno/etc/certificate/system/default/
cert.pem chain.pem fullchain.pem privkey.pem
root@phong:/# openssl x509 -in /usr/syno/etc/certificate/system/default/cert.pem -text
Example dockerd.json configuration that will use the default Synology certificate and chain in DSM.
{
"data-root" : "/var/packages/Docker/target/docker",
"log-driver" : "db",
"registry-mirrors" : [],
"storage-driver" : "btrfs",
"hosts" : [
"unix:///var/run/docker.sock",
"tcp://0.0.0.0:2376"
],
"tlsverify" : true,
"tlscacert" : "/usr/syno/etc/certificate/system/default/chain.pem",
"tlscert" : "/usr/syno/etc/certificate/system/default/cert.pem",
"tlskey" : "/usr/syno/etc/certificate/system/default/privkey.pem"
}
If you want to only allow clients with issued certifcates to connect, set the tlsverify to true.
Note, you should remove any entry in hosts to ports 2375 as this will prevent the docker daemon from starting.
~/ docker --tlsverify --tlscacert=ca.pem --tlscert=cert.pem --tlskey=key.pem -H=phong.cormier.local:2376 version
In my case I copy the certificates (ca,cert,key) to ~/.docker/ for easying the use on the command line and keyboards :)
~/ mkdir -pv ~/.docker
~/ cp -v {ca,cert,key}.pem ~/.docker
~/ export DOCKER_HOST=tcp://phong.cormier.local:2376 DOCKER_TLS_VERIFY=1
If you don’t do this or your situation calls for a different CA certificate, you can use the tlscacert argument.
~/ docker --tls image ls
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
nginx latest 35c43ace9216 3 days ago 133MB
grafana/grafana latest db33d19bd973 3 days ago 198MB
amazon/aws-cli latest caf8d46b3369 4 days ago 294MB
postgis/postgis latest 563a1a69fd0d 5 days ago 491MB
gitlab/gitlab-runner latest e297d453ec30 4 weeks ago 513MB
microsoft/azure-cli latest 8bcd2e2ef062 4 months ago 711MB
This is a more secure setup. Secure traffic in transit and authenticate clients with certificates.
Docker Command Examples
Some basic commands to run, attach, and exec on containers using Docker API endpoint. For example, to list containers.
You can pass the endpoint information on the command using -H parameter, but the docker command also honours the environment variable DOCKER_HOST.
~/ export DOCKER_HOST="tcp://192.168.0.10:2375"
Or if you are connecting to secure endpoint, use FQDN/hostname…
~/ export DOCKER_HOST="tcp://phong.cormier.local:2375"
Now you can use docker commands as you would if docker was running locally.
~/ docker container ls
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
9c1be7f52ef3 microsoft/azure-cli:latest "/bin/sh -c bash" 17 hours ago Up 26 minutes ms-azure-cli
~/
Run a container and execute a given command
~/ docker run amazon/aws-cli:latest --version
aws-cli/2.1.27 Python/3.7.3 Linux/4.4.59+ docker/x86_64.amzn.2 prompt/off
~/
How to attach to existing container
~/ docker attach ms-azure-cli
bash-5.0# az --version
azure-cli 2.19.1
You can detach from the container without stopping the container by using a keyboard shortcut, much like you would to unfocus your mouse from a virtual machine terminal applicaiton. Pressing Ctrl-P + Ctrl-Q will detach from the container, I had to also press Ctrl-C to completely return to my shell, not sure why this is the case.
If you just want to execute a simple command inside a running container exec is the Docker command you want to use
~/ docker exec ms-azure-cli az --version
Please let us know how we are doing: https://aka.ms/azureclihats
and let us know if you're interested in trying out our newest features: https://aka.ms/CLIUXstudy
azure-cli 2.19.1
core 2.19.1
telemetry 1.0.6
Troubleshooting
Connect to FQDN
If you encounter warnings like the following, connect using the FQDN of certificate you set Docker to use, instead of the IP address, which you might have been using during a concept plaintext setup.
~/ docker image list
error during connect: Get https://192.168.0.10:2376/v1.24/images/json: x509: cannot validate certificate for 192.168.0.10 because it doesn't contain any IP SANs
~/ export DOCKER_HOST="tcp://phong.cormier.local:2376"
~/ docker image list
Restart Server Daemon
I changed the certificate and ran in into an issue that error of incompatible key usage kept my docker client from connecting. Even though the API seemed to be offering up the correct certificate, verifying with the command openssl s_client.
error during connect: Get https://phong.hq.cormier.co:2376/v1.24/events: x509: certificate specifies an incompatible key usage
After restarging the server docker daemon, I will able to connect successfully.
Conclusion
This setup gets you a quick, although not the cheapest solution for Linux Docker containers.



